Clinical Image
Hypokalemic Nephropathy as a Form of Presentation of Adrenal Carcinoma
Guillermo Flores*, Luis I Cobas and Andrea González-Morales
Section of Internal Medicine, Department of Medicine, Hospital de Especialidades del Centro Médico Nacional
Siglo XXI, Instituto Nacional del Seguro Social and Facultad de Medicina de la Universidad Nacional Autónoma de
México
*Corresponding author: Guillermo Flores, Servicio de Medicina Interna, Hospital de Especialidades del Centro Médico Nacional Siglo XXI, Avenida Cuauhtémoc # 330. Colonia Doctores, Mexico City, 06720, Mexico
Published: 09 Nov, 2017
Cite this article as: Flores G, Cobas LI , González-Morales
A. Hypokalemic Nephropathy as a Form
of Presentation of Adrenal Carcinoma.
Ann Clin Case Rep. 2017; 2: 1458.
Clinical Image
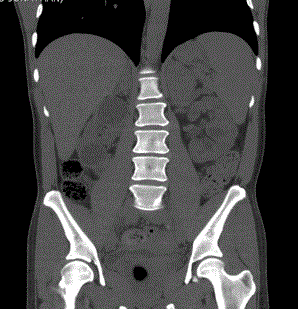
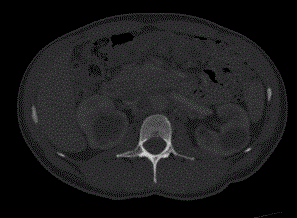
A 29 year-old Mexican mestizo male was referred for long standing hypertension, chronic renal failure and chronic hypokalemia. Three years before he was diagnosed with systemic hypertension and since then he had hypokalemia that required high doses of potassium chloride as well as chloride resistant metabolic alkalosis. One year before he had a stroke. Upon admission he persisted with hypokalemia. Plasma Aldoterone Concentration (PAC) and Plasma Renin Activity (PRA) index (ARR) was > 200 with a PAC of 150 pg/mL. Saline loading and oral salt-loading tests were confirmatory of primary aldosteronism. A CT-scan demonstrated bilateral enlarged adrenal glands with an ovoid shaped mass of 4.5 X 3.5 cm on the left adrenal gland (Figure 1). CT scan showed multiple bilateral medullary cysts (Figure 1 and 2). Laparoscopic left adrenalectomy was performed and histological findings were compatible with adrenal carcinoma. We conclude that chronic hypokalemia is accompanied by enhanced adrenal cystogenesis and may lead to interstitial scarring and renal insufficiency.
Figure 1
Figure 1
A CT-scan demonstrated bilateral enlarged adrenal glands with an ovoid shaped mass on the left
adrenal gland.