Clinical Image
Successful Treatment of Lung Abscess with Pigtailed Catheter after Failure with Antibiotics and Surgical Debridement
Dalvir Gill1* and James Sexton2
1Department of Internal Medicine, SUNY Upstate Medical University, USA
2Department of Infectious Disease, SUNY Upstate Medical University, USA
*Corresponding author: Dalvir Gill, Department of Internal Medicine, SUNY Upstate Medical University, 750 East Adams Street, Syracuse, NY, 13210, 60 Presidential Plaza, Apartment 1104, Syracuse, 13202, USA
Published: 06 Feb, 2017
Cite this article as: Gill D, Sexton J. Successful Treatment
of Lung Abscess with Pigtailed Catheter
after Failure with Antibiotics and
Surgical Debridement. Ann Clin Case
Rep. 2017; 2: 1257.
Clinical Image
Necrotizing pneumonia is a rare complication of pneumonia as it could lead to lung abscess,
septic shock and respiratory failure. 80-90% of lung abscess are successfully treated with antibiotics,
however surgical intervention is required in refractory cases [1]. Mortality rates are high despite thoracotomy and lobectomy, ranging from 15-20% [1]. An alternative therapy is percutaneous tube drainage.
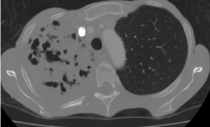
We present a summary of events in a case of complicated necrotizing pneumonia (Figure 1).
Our patient is a 58-year-old female with past medical history significant for COPD, who initially
presented with productive cough, fever, chills, and shortness of breath. Her vitals remained stable
and physical exam was remarkable for dullness on percussion and decreased breath signs of the
right upper lung fields. Chest X-ray showed right apical consolidation and follow up CT thorax
showed large cavitary mass that involved the upper lobe of the right lung and the superior segment
of the right lower lobe. Bronchoscopy with biopsy was consistent with necrotizing pneumonia and
patient was treated with IV antibiotics. However her symptoms did not resolve and surgery was
consulted. Patient got de-cortication of the right upper lobe. Nonetheless, surgical intervention did
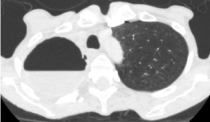
not help and she was readmitted. Compared with prior CT thorax, now there was a substantial
complex fluid within the cavity, suspicious for a superimposed infection in the right apex (Figure
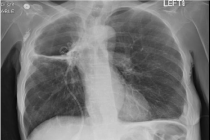
2). She was started on IV antibiotics again, but her symptoms persisted. Chest tube was placed with drainage of purulent discharge (Figure 3). The cultures grew pansensitive
Klebsiella pneumoniae, which was treated with antibiotics.
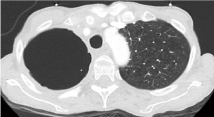
Repeat CT thorax in 2 months showed persistent cavity in the right
upper lobe but the air/fluid level had resolved (Figure 4).
Necrotizing pneumonia is a complication of pneumonia and it
could be fatal if not treated appropriately. Klebsiella pneumoniae is
a common cause of necrotizing pneumonia and is often complicated
by lung abscess, which usually appears as cavities. One case series
demonstrated multiple small cavities ranging from1 mm - 3 cm
in 48% patients by CT thorax [2]. The most feared complication is
massive pulmonary gangrene, which could develop from lung abscess
from Klebsiella pneumoniae, and it can destroy an entire section of a
lung. Although pulmonary gangrene is a rare condition, but over onehalf
of cases are attributable to Klebsiella pneumonia [2]. On imaging,
pulmonary gangrene starts with lung consolidation, which then leads
to multiple small cavities that coalesce into one large cavity. After a
10–14-day period of conservative medical therapy without clinical
improvement, percutaneous tube drainage should be considered.
Necrotizing pneumonia secondary to Klebsiella pneumonia could
lead to fatal pulmonary gangrene. Percutaneous tube drainage is a
safe and effective method for treating lung abscesses, and it should
be strongly considered in complicated patients who have failed
trial of antibiotics. The evidence for such therapy is derived from
uncontrolled case series, and the need for randomized trials cannot
be emphasized enough.
Figure 1
Figure 2
Figure 2
Compared with prior CT thorax, now there was a substantial complex fluid within the cavity, suspicious
for a superimposed infection in the right apex.
Figure 3
Figure 4
Figure 4
Repeat CT thorax in 2 months showed persistent cavity in the right
upper lobe but the air/fluid level had resolved.