Clinical Image
Trichosporon Fungemia in a Patient with Acute Myeloid Leukemia
Nakase K1*, Fujieda A2, Umino A2 and Katayama N2
1Cancer Center, Mie University Hospital, Tsu, Japan
2Department of Hematology and Oncology, Mie University Hospital, Japan
*Corresponding author: Kazunori Nakase, Cancer Center, Mie University Hospital, 2-174 Edobashi, Tsu, Mie 514-8507, Japan
Published: 07 Jul, 2016
Cite this article as: Nakase K, Fujieda A, Umino A,
Katayama N. Trichosporon Fungemia in
a Patient with Acute Myeloid Leukemia.
Ann Clin Case Rep. 2016; 1: 1036.
Clinical Image
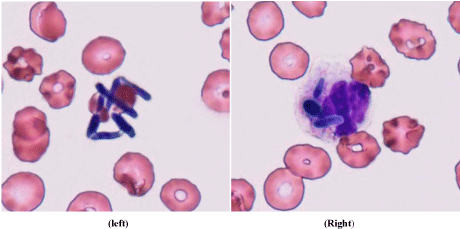
A 58-year-old man with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) received allogeneic peripheral blood stem cell transplantation from his HLA-matched sister. After transplantation, he suffered grade II graft-versus-host disease (skin), and severe diarrhea probably due to intestinal thrombotic microangiopathy. Various immunosuppressive and antithrombotic therapies were performed for these symptoms. Three months later, he developed sepsis due to trichosporon species. As micafungin had been given since the time of preconditioning for transplantation as an antifungal prophylaxis, the agent was changed to liposomal amphotericin B. However, he died 3 days after that. On the day of his death, numerous fungi (Figure 1, Left) and fungal phagocytosis by neutrophils (Figure 1, Right) were found on his peripheral blood smear sample. This case was a breakthrough trichosporon fungemia [1], in a patient with AML receiving micafungin.
Figure 1
Figure 1
Peripheral blood smear sample showing trichosporon fungemia (×1000, May-Giemsa stain).
Left: Aggregation of fungi.
Right: Fungal phagocytosis by a neutrophil.